Banking has always been about trust. There was a time when customers visited a bank branch, stood in line, and waited days to approve a transaction. Today's banking experience is incredibly different. The moment you open your mobile banking app, your money transfers in seconds, you're alerted instantly to fraud, and you receive investment advice. Behind the scenes, one silent engine powers all of these outcomes, which is Artificial Intelligence (AI).
My first real experience with AI in banking was with a mid-sized private bank that utilized an AI-powered system to review and verify Loan documentation. I was curious about this technology and monitored the bank's progress as they reduced manual effort, improved accuracy, and moved from days to hours in processing time. The result was happier customers, less stress among bankers, and the finance team spending more time on real analysis versus paperwork. This was a transformative moment that demonstrated how AI could change the operating model of a bank.
In this article, I will share about what AI in banking really is, how banks are using it, the benefits, challenges, and the future of AI in banking.
Quick Summary
AI is revolutionizing banking as we know it today. Banks can utilize AI tools to automate routine tasks, improve security, and establish a greater understanding of customer needs to replace slow manual processes. AI enables banks to render large samples of data in a matter of seconds, discover suspicious fraud before it emerges as a legitimate threat, and develop personalized financial products that are based on money movements based on habits. The incorporation of AI into banking means factors like loan approval times, customer service, fraud detection, and investment advice become smarter and faster.
AI technology helps banks build stronger and more meaningful relationships with customers, drives organizational efficiency and risk reduction, and embraces competition in an increasingly competitive digital market environment. Some all of this is to have a more human feel to the future of banking when in fact much of the future workload is conducted by machines.
Our focus in this article:
1. How are AI systems involved in banking operations?
2. Why are AI models required for banking operations?
3. What benefits do banks receive from AI?
4. How do AI agents prevent fraudulent activities?
5. What are the future trends of AI models in banking?
What is Artificial Intelligence in Banking?
When we say AI in banking, we mean technology that is able to "think" like a human being, analyse data, recognize patterns, make predictions, and even interact with humans. One way to conceptualise this power is to think of the enormous amounts of data that banks collect: transaction records, spending habits, loan histories, credit scores, financial goals, and so forth. Traditionally, examining that data manually and deriving meaningful insights from it is overwhelmingly labour-intensive and takes a long time. AI systems are now able to analyze all of this information in an instant and provide meaningful insights.
For example, rather than having a banker review each loan document on a case-by-case basis, an AI tool can review, extract critical details, verify your identity, assess your level of risk, and recommend a decision, likely much faster than any person could.
Similarly, you no longer have to wait for a customer to report fraud; AI models can immediately detect unusual behaviour, interactively notify customers, and provide them with an overall better experience. This is the level of intelligence and automation that can only be described as AI in banking.
Additionally, AI drives the belief to know customers. If someone is habitually late on bills or withdrawing cash frequently, an AI-driven banking service can highlight them for financial III advice or special rates. Similarly, if someone's spending habits show they fly frequently for business, their banking experience will include recommendations for certain travel credit cards. Technology makes our lives easier while empowering a more proactive customer experience.
Banks are utilizing diverse forms of AI technology, such as
- Machine learning techniques for pattern recognition and risk prediction
- Natural language processing will help understand conversations with customers
- Generative AI can be employed to assist in personalized communication
- Predictive analytics capabilities to predict future behaviour
AI systems, tool organized and interpret complicated information, allow banks to deliver services with increased precision and efficiency. In a lot of ways, AI is evolving into the "brain" of the contemporary financial ecosystem.
Why AI Matters to Financial Services Organizations
In recent years, financial services organizations have recognized that contemporary customers seek not just banking, but smart banking. Customers expect their banking services to be fast, secure, and personalized, available at any time and from anywhere. Only AI can provide this at scale.
Throughout my time working at banks, I have observed that internal teams often spend the majority of their time on time-consuming and repetitive tasks such as data entry, manual verification, regulator compliance checks, and customer inquiries.
But when it comes to AI, it is like a trusted teammate that never gets tired. AI can take over these repetitive tasks, thus allowing the staff to attend to customer relationships or decision-making. AI is also important since the financial services industry is highly regulated. Since banks are dealing with sensitive data, even the smallest error could lead to large losses or expensive lawsuits. AI helps mitigate these risks through continuous monitoring of the data, developing an understanding of transaction trends, and immediately flagging when anomalies occur.
-
How AI improves the security of banking operations
AI enhances compliance and security. One last reason that AI is important to financial services organizations is customer retention. The evidence demonstrates that people will remain loyal to banks that accurately help them manage their money. AI can provide these types of behavioural insights or recommendations through intelligent means, such as forecasting budgets, sending reminders to make payments, suggesting investments, or notifying customers of excessive spending.
Customers feel more engaged and informed with personalized insights, driving better loyalty to the bank.
-
Global Ai Based Fintech Startups
Another area of competition stems from USA fintech start-ups like Stripe, Google Pay, which have already aggressively deployed AI to create faster and better systems. Traditional banks will need to use AI to achieve the same level of innovation and to defend against falling behind the proverbial eight ball. The change is so advanced today that organizations are leveraging an "AI-first" mentality, which means they are hoping to design new products and strategies surrounding AI.
Core Use Cases of AI in Banking
AI has quietly secured the position of being one of the most important employees inside modern banks. It works around the clock, makes accurate decisions, and extracts learning from every interaction, all while being a member of your organization. Whether it is enhancing customer service or detecting fraud, the applications of AI are far-reaching and very practical.
Let me share my experiences with some of the most compelling applications of this type of technology.
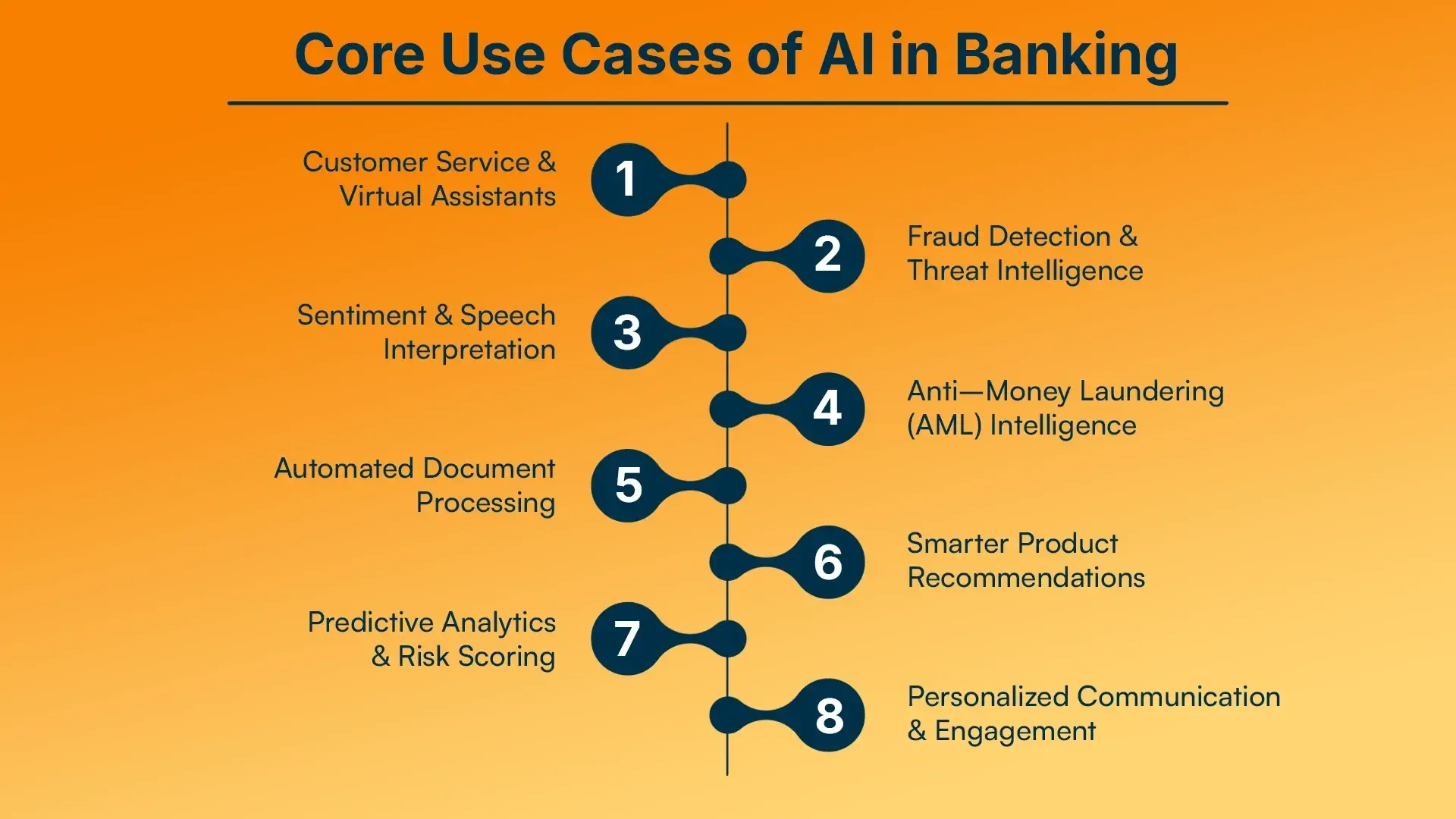
1. Customer Service & Virtual Assistants
Before AI was adopted, customer service in banks often included long wait times, transfers to different departments, and issues left unresolved. Intelligent chatbots and voice assistants now turn this paradigm upside down.
These systems can instantly respond to everyday questions like:
- "What is my current balance?"
- "When is my credit card payment due?"
- "How do I update my address?"
One example of this was a bank I worked with, which implemented an AI chatbot in its web and mobile apps. Support requests were able to decline in a couple of weeks after the chatbot was launched because nearly 65% of basic questions were answered instantaneously without the need to speak to a human agent.
Customers enjoyed the experience because they never felt rushed or ignored; they could get answers any time they needed, even at midnight.
But that doesn't mean this model replaces human support; it simply enables human agents to spend their time on the complex, emotional exchanges requiring true empathy.
2. Fraud Detection & Threat Intelligence
Fraud is more sophisticated in banking today than ever. The worst part? Many of the attacks now also utilize AI. Fortunately, banks are now taking the fight to the next level by implementing AI systems of their own.
AI scans patterns of behaviour, spending location, time, device IDs, login behaviours and quickly raises the alarm when something is out of the ordinary.
A notable example: A friend of mine suddenly received a message that his card was temporarily locked. The attempt to use it from another country triggered the system. Within moments, the bank had already responded, stopping a potential loss. After hearing about this encounter, he told me that this incident made him trust the bank more than any offer or cash back had ever done. If you have used UPI, you must have noticed this security feature, where AI intelligence gives you a warning when you make a payment while on a call.
That is the beauty of AI, that it detects fraud before the harm is done. The old rule-based systems only identify fixed boundaries, while AI continues to learn and improve its accuracy every day, learning from outcomes.
3. Sentiment & Speech Interpretation
Banks receive thousands of calls each day. Analyzing conversations to find emotions, discontent, or other needs is outside human capability.
Then there are AI listening applications.
AI listens to calls for us, turning speech into text, determining tone, and identifying if the customer is:
- Frustrated
- Confused
- Happy
- Ready to close an account
In the last year, I did a project for a financial institution that studied customer sentiment, and, somewhat surprisingly, the AI uncovered patterns even a human agent would not have found. It identified polite customers who were dissatisfied but did not appear to be frustrated. The bank proactively called these customers, resolved problems, and thus reduced churn. It was as if a beyond-smart psychologist was just sitting inside a call centre.
4. Anti-Money Laundering (AML) Intelligence
Money laundering networks are incredibly complex, and it is slow and often inaccurate to manually identify illicit activity.
AI assists compliance teams in scanning complex transactional webs to quickly identify anomalies and uncover hidden relationships. It uses algorithms for behaviours such as large dollar amounts suddenly being transacted foreign transfer chains, silent but previously active accounts suddenly moving money early identification of suspicious threads.
I've observed that banks using AI for AML not only identify more legitimate threats, but also see a reduction in false alerts. This saves thousands of hours of staff time and enables teams to focus on genuine risk.
5. Automated Document Processing
Account opening, KYC, loan documents, paperwork everywhere. Once upon a time, verification and data entry took days. Now, AI can scan, extract information, validate identity, and classify documents in a matter of minutes.
I witnessed this revolution firsthand in a bank, where loan document review time was reduced from 3 working days to a few hours.
Accuracy improved so much that internal audits recorded the number of manual errors decreasing.
Customers received approvals much faster than before, and employees could finally breathe as they were able to complete meaningful work instead of struggling with piles of files.
6. Smarter Product Recommendations
Gone are the days when all banks would push the same savings account or credit card to all customers. AI examines a customer's lifestyle, spending habits, age, job, investment style, and money priorities in the recommendations that will help them the most.
It doesn't feel like marketing; it feels more directive toward individual needs, which means better financial decisions and a deeper level of trust.
7. Predictive Analytics & Risk Scoring
The power of AI lies in its ability to make future predictions regarding anything from which loan applicants are likely to default to an impending downturn in the economy. AI can utilise data points that would've been rejected in the traditional creditworthiness determinations. In lieu of solely considering an applicant's credit, AIs can factor things like:
- Their bill payment history
- Their spending patterns/ cycles
- Their employment history
This allows banks the opportunity to provide credit to more people, responsibly, than they would typically be able to, further promoting financial inclusion.
I have seen many teams use AI-based scoring to classify risk in a more normalised representation or fashion. Over a period of time, doing so eventually lowered defaults and allowed the banks to help more individuals who do not fit the profile of traditional credit applicants.
8. Personalized Communication & Engagement
AI banks have made banking feel less transactional and much more relational in nature. AI considerations are utilized to monitor spending, upcoming dues, and overall financial responsibility, then "nudges" the user accordingly.
For example: "You have spent more on dining this month, you may want to adjust your spending budget." This type of nudge feels like a friendly counsellor gently reminding you to take control of your finances, or a friend just thinking about you.
These types of features remind a user of their relationship with their banker, and the importance as it relates to their overall financial experience, which makes banking feel meaningful again.
Also Read: How AI Is Transforming Digital Payments
Advantages of Artificial Intelligence in Banking
Now, let's take a look at the practical results. These are benefits I have personally witnessed at multiple institutions that adopted AI in a serious way.
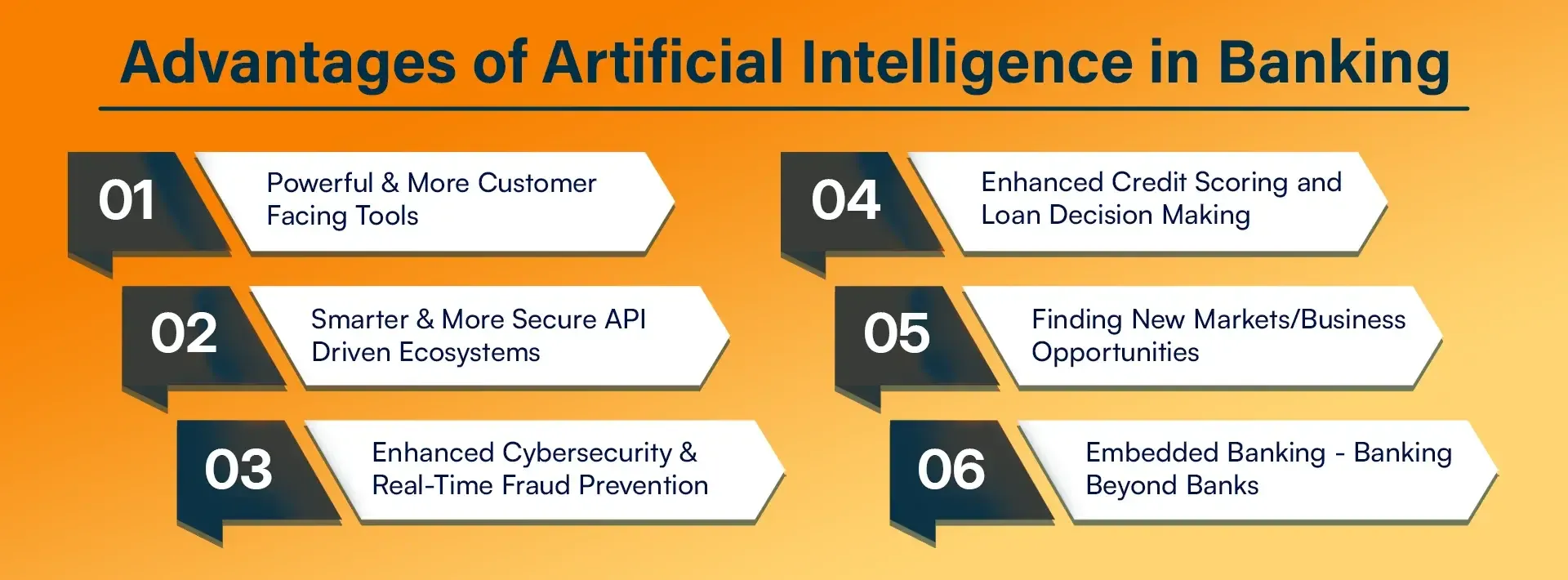
1. Powerful & More Customer-Facing Tools
AI makes banking experience feel more human and less abstract. Robo-advisors help the user to better plan savings, chatbots answer questions immediately, and personalized dashboards give real insight into spending.
What I like the most is how AI supports people who do not inherently understand finance. Someone who was previously scared to manage his or her money could now receive simple, friendly advice at any time. This opens up financial literacy for everyone and builds customer confidence.
2. Smarter & More Secure API-Driven Ecosystems
Banking is so connected today, with payment apps, investing platforms, e-commerce wallets, and more. APIs act as a sort of bridge between multiple technology stacks.
AI strengthens these bridges by:
- Monitoring for suspicious activity
- Automating surveillance checks
- Improving data sharing
- Getting to the bottom of downtime
I was a partner at one bank managing hundreds of third-party integrations. After adding AI-driven monitoring, the breakdowns of integrations and security incidents became noticeably less frequent.
It created a cleaner, more trusted digital marketplace. When APIs get smarter, everything around them gets smarter: customer experience, reliability, and innovation.
3. Enhanced Cybersecurity & Real-Time Fraud Prevention
If there is one use case where AI has really proven itself as a necessity, it is security.
Fraud has gotten more sophisticated, as attackers utilize spoofs, deepfakes, and social engineering. I will never forget the first time I saw AI integrated into the security of a bank; I was actually wowed. It monitored behaviour continuously, not just the transaction, but the entire usage behaviour of the user.
For instance, if you transact in one city all the time, and then a transaction is attempted from overseas at a late hour, AI would bring it to the attention of the security team immediately. In some banks I have worked with, the system would alert the customer, as well as limit access, providing verification.
The models scanned millions of data points in a split second:
- Device fingerprinting
- When you made a login
- What type of transaction did you make
- Geolocation
- Connection type
- Your history
This gave banks the ability to address suspicious activity long before the customer notices something was wrong.
I recall a time when a corporate account was the target of multiple password resets. AI flagged the unusual signatures of the requests, which prevented unauthorised access. The company later told me this probably saved them millions.
4. Enhanced Credit Scoring and Loan Decision Making
Credit scoring was traditionally based on strictly past financial behaviour. This unfortunately excluded many qualified borrowers, freelancers, young professionals, entrepreneurs, and other emerging borrowers.
AI provides a second chance solvent. It is able to analyse dozens of alternative indicators, such as:
- Bill payment frequency
- Spending profile
- Job history
- Savings
- Previous bank interactions with the institution
- Industry
- Overall transaction health between deposits and withdrawals.
With this information, banks can more accurately (and fairly) assess risk and provide credit to the types of borrowers who might have been rejected previously.
In one project I worked on, the AI did not simply provide an "approved" or "denied" forecast, but rather profiled each of the applicants into more nuanced categories. Borrowers with a less-than-desirable credit history but favourable spending patterns, for instance, had specified terms prepared for them; many times, an "approval" was not necessary due to the credit score account.
These are reduced biases
- Improved loan approvals
- Lowered NPAs (defaults)
- Expanded financial access
It began to feel more like an assessment than a system; the AI was ultimately better than a banker and able to assess even more accurate and newer data.
AI-based credit models provide a fairer, faster, and reliable way to provide financial resources to individuals when they need them.
5. Finding New Markets/Business Opportunities
AI does not just automate work; it identifies opportunities beyond what we can see.
Banks possess a tremendous amount of data, but data without context is not useful. AI produces actionable insights to help strategise based on data. It can examine:
- Patterns of customer inactivity
- Areas of unmet investment
- Trend shifts in the rate of savings
- Which customers are most likely to close their accounts
- Areas of increased loan demand
I've worked alongside teams where AI highlighted clusters of customers showing early signs of churn, less frequent logins, reduced deposits, and less engagement with offers were all early indicators. The bank leveraged AI to reach out with tailored benefits, while many accounts were retained.
Predictive analysis can similarly tell banks where they should establish branches, what new product they should build, or even what group of customers are most in need of credit flexibility.
The use of AI is how banks can engage in intelligent growth; they don't simply pursue customers, they know them. This transition from intuition-based thinking and strategising to data-driven analytics plays a significant role in AI as the new growth engine.
6. Embedded Banking - Banking Beyond Banks
Embedded banking is an interesting concept that seamlessly integrates financial service capabilities into everyday non-bank platforms.
Consider the ways that Starbucks, Amazon, or travel apps have enabled their customers to store money, make a payment or utilise credit all before they even enter into the bank.
That's embedded banking. The impact of AI in embedded banking is significant, as it can:
- Help brands understand customer behaviour
- Evaluate a customer's creditworthiness
- Predict risk
- Securely manage transactions
- Customise offers on the platform
I recall considering a retail platform that was exploring the potential of implementing AI micro-credit capabilities at checkout. They would instantly qualify their customer based on frequency of purchase, whether payments were made in full and on time, and category. Even in the absence of a credit score, the retailer would extend small credit pockets to their customers to enable them to shop.
In this manner, banking became invisible; it is integrated rather than separate. Customers receive the convenience; banks and brands share the profit. It is a thoughtful advancement that has enabled banking to become more intertwined with your lifestyle.
Challenges & Risks of AI in Banking
Despite its transformative potential, AI systems come with their own imperfections. I've seen banks run into issues that require deliberate planning and governance. As a corollary, let's look into some of the real-world problems.
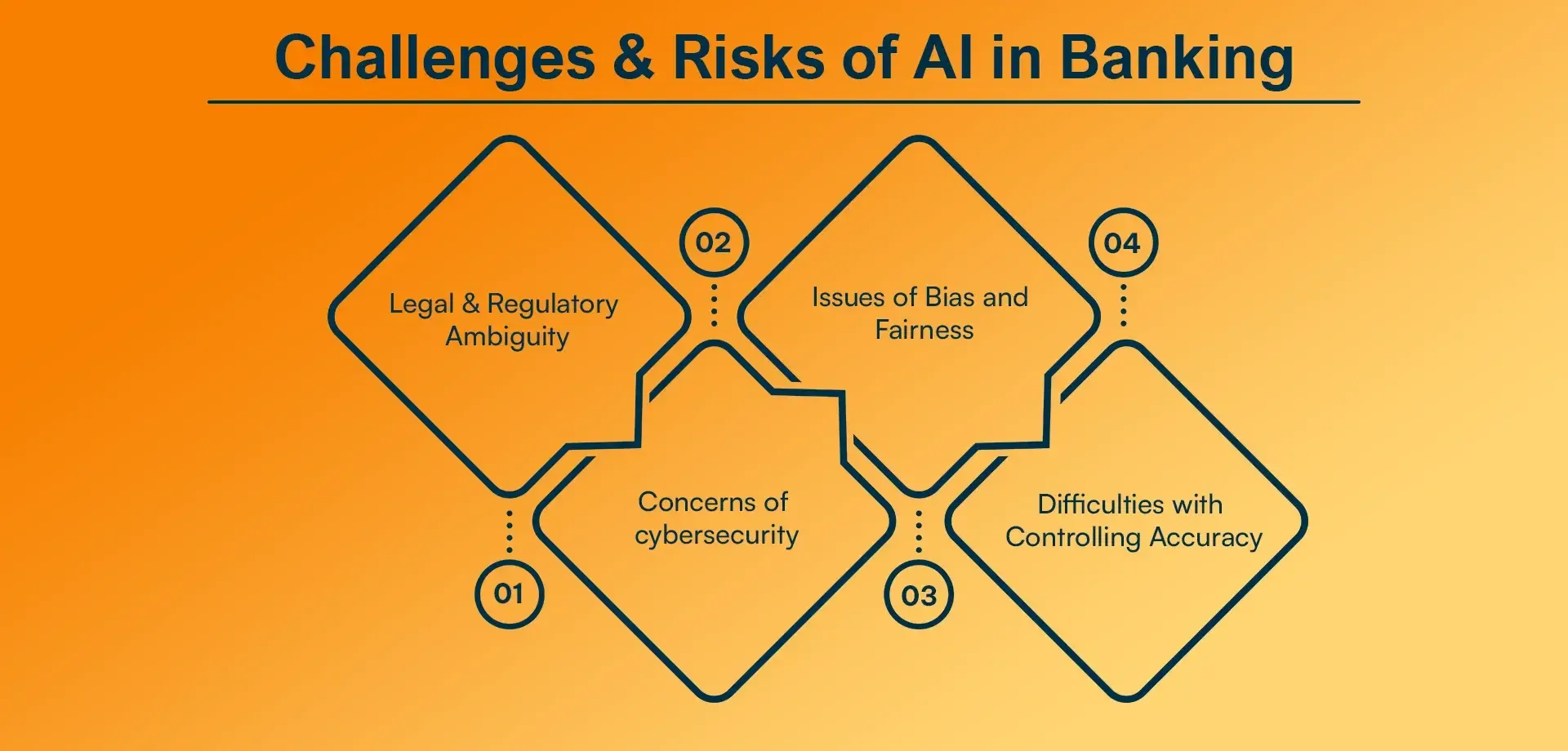
1. Legal & Regulatory Ambiguity
AI models gain information from large datasets (or public information). Whether or not the use of specific datasets or training models on third-party information is legal is not yet a clear concept in many countries.
For instance, during one implementation, legal teams spent months defining what data could legally be used to engage AI to train the model. Without adequate governance, banks risk becoming embroiled in:
- Copyright infringement
- Data misuse
- Non-compliance
This is one reason why regulatory functions are going to be necessary; this means each bank will have to create inside policies, all under its own governance, all to avoid some larger regulatory frameworks.
2. Concerns of cybersecurity
AI not only increases the defences of banks, but ironically, it also increases the attack surfaces for adversaries. In 2024 alone, the state of California in the USA suffered losses of $2,539 billion due to cyberattacks. Therefore, securing banking systems through the involvement of AI is crucial, as banking is the backbone of any country's economy.
Some of the techniques a sophisticated attacker may try are:
- Manipulate Models
- Poison Data
- Fake content for sophisticated spoofing (tracks or transactions)
- Reverse engineer their methodology for identifying fraud and privileged security.
AI models contain high-powered financial logic; thus, they are highly valued targets.
Banks have to worry about securing customer accounts, but also the security of the AI models against attacks as in the other example.
This means that in addition to customer accounts, banks also have to secure
- Secure Data Pipelines
- Secure Comms
- Access control
- Monitoring
- Politics or ethical means to moderate.
Just utilizing AI does not ensure any trust factor; you have to deal with the maintenance of the AI, but with a high level of security.
3. Issues of Bias and Fairness
Fairness is solely based on the historical data that trained the algorithm. The algorithm will create, with no awareness, the same bias reflected in the historical data it was provided.
For example, with credit scoring models I've seen once we reviewed those scoring models, they behaved unfairly towards gig workers. The models did not account for gig workers' income very well. Once those scoring models were retrained on broader data, those scoring models were made more accurate.
Banks need to have systems in place to mitigate risk and monitor AI for fair and inclusive outcomes.
4. Difficulties with Controlling Accuracy
AI algorithms do not have transparency in their decision-making processes. AI does not "think", it detects patterns. This pattern detection can lead to the following:
- Making incorrect predictions
- Giving over-confident answers in the faulty outputs.
Plus, it can be exceedingly difficult to explain to someone what the reasoning was behind the prediction to begin with. When it comes to banking, the need for transparency is great.
The Future of AI in Banking
In my opinion, AI will not be a passing fad for banks; it will establish the framework for banking in a new era. During my first experiences with financial teams, AI was considered an experimental add-on. Today, it has taken centre stage in any conversation surrounding growth, risk, or customer experience.
Banking will be AI-driven, customer-centric, and ultimately invisible, as most financial interactions will take place in the background of our lives.

1. AI-First Banking Will Be the Standard
Before long, every major bank will move from using AI to being built around AI. Decisions regarding a new product, pricing, or even a credit decision will start with AI insight, rather than end with it.
I see this as happening already; internal dashboards provide AI-based insights instantaneously around revenue, risk exposure, or changes in regulations that are coming down the pike. The speed of decisions is mind-boggling.
In an AI-first world, banking leaders will pull real-time models of data rather than static reports. In the outcome, we see smarter strategies, faster innovation, and better leaders.
2. Highly Personalized Experiences
Picture logging into your bank app, and instantaneously, everything is personalized for you. Suggestions for savings, investment opportunities, and friendly feedback messages, based on data collected about you, will be there. This is not a dream, but the next generation of personalisation powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
Not long ago, I was working on a project with a financial services organization where we were testing an AI model that was predicting user intents in the app experience.
For example, if a user viewed home loans multiple times but did not apply, the app would provide education about (EMI calculations and eligibility) that the user viewed directly in the application. As a result, we saw incredible jumps in engagement rates.
Micro-personalisation like this will only become more commonplace. Soon, banks will not only "serve customers." They will have a deeper understanding of the customer as an individual to anticipate needs before the customer even knows they have them.
3. Enhanced Human-AI Collaboration
The best banks will not eliminate humans, but will elevate them. AI will automate and manage repetitive, data-driven tasks while humans will have time to use judgment, empathy, and strategy.
For example, imagine a relationship manager uses an AI dashboard to see instantly the complete financial behaviour patterns of a client (including preferences and risk indicators). Instead of spending hours on prep work, the relationship manager will have a deep one-on-one conversation within minutes.
A future where organisations combine the capabilities of human warmth and AI precision will be the future of banking. It is not too far from there.
4. Responsible & Ethical AI Will Be a Priority
As AI becomes more capable, banks will have an increased duty to ensure it is used responsibly. They will need to provide:
- Industry-standard rationale for decision-making
- Clear rationale for automated interactions
- Fair treatment across demographic lines
- Strong data privacy and protection
I believe the companies that invest in responsible governance today will win tomorrow. Consumers will not only choose banks because of money, but also because of the security being taken around their data.
5. Embedded & Invisible Banking
We are venturing into a world where banking is happening regardless of whether you notice. Voice-activated transfers from your phone and AI lending options built into shopping apps will incorporate financial services seamlessly into daily living.
In a few short years, you may book a flight and in seconds, your digital wallet offers travel insurance. And currency conversions. And a cashback credit. You will not open a banking app. The banking app will open in front of you.
This is the type of seamless, intelligent future AI is building, and we are just starting to reach the beginning.
Conclusion
If I had to sum up AI in banking in one line, it would be this: AI doesn't replace banking; it reimagines it. From automating repetitive workflows to helping customers feel understood, AI is creating a world where finance becomes faster, safer, and more human.
Having worked closely with these technologies, I've seen how they make both employees and customers happier. Tasks that once took hours now finish in seconds. Fraud that once went unnoticed is now caught instantly. And decisions once made on gut feeling are now guided by precision data. Of course, challenges remain bias, regulation, and security, but these are not roadblocks; they're reminders to innovate responsibly.
Additionally, if you want to implement a custom AI-driven payment or software system in your business systems, you can contact a trusted firm like Rejoicehub. Because the future belongs to banks and payments that learn, adapt, and build with AI at their core.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What role does AI play in banking?
AI automates routine tasks, anticipates risk, identifies fraud, and customises customer service. Artificial intelligence helps banks do things smarter and faster for customers.
2. In what way is AI enhancing customer service?
AI provides instant answers and round-the-clock servicing through chatbots, voice assistants, and intelligent automation, freeing human agents to spend their time on complex questions.
3. Is AI making banking safer?
Yes. AI monitors transactions continuously, recognises suspicious behaviour, and stops fraudulent activity as it happens, often before the customer figures it out.
4. What AI applications are being used by banks today?
AI is being leveraged for credit scoring, document processing, anti-money laundering (AML), anomaly detection, and product recommendations for customers personalized to them.
5. Can AI decrease the risk of loan defaults?
Definitely, Predictive models can identify and alert applicants that they pose a risk as early as the loan application, all the way through the loan cycle, and offer suggestions to help reduce their risk if they follow responsible lending.
6. How does AI affect customer trust?
AI builds trust by providing consistent accuracy, personalised advice, and rapid response as long as it is ethical and transparent.
7. What are the biggest risks to be considered when using AI at banks?
Banks need to be cautious around ambiguity in the law, cybersecurity, data bias, and lack of explainability.
8. Is it true that AI will replace bankers?
No, AI addresses repetitive tasks; however, it will not replace human judgment, empathy, and strategic understanding, because the greatest outcomes will emerge from the teamwork of humans and AI.
9. What makes AI more capable of fraud detection when compared to traditional systems?
Traditional systems operate based on rules, while AI systems learn and adapt from previous patterns, allowing them to identify emerging types of fraud in real time and far more quickly.
10. What do we mean by embedded banking, and where does AI fit in?
Embedded banking is when banking products and services are accessed through platforms that are not banks. AI can help assess risk in real-time and also provide personalization for all transactions without having to leave the app, to make a secure transaction.
