AI has become the backbone of many technologies which might be used by us on a daily basis. Ever thought about how your phone knows your preferences or how robots can make split-second decisions? This is known as Agents in Artificial Intelligence. AI agents can handle tasks, analyze data, and can even make decisions. That also without human interference.
I guess you might have experienced Google Maps suggesting the fastest route while avoiding traffic. Behind this is an AI agent. These agents are truly commendable. They can simplify most of the things. AI agents are systems designed to observe their environment, process data, and take actions to achieve specific goals. That can be simple reflex agents to complex multi-agent systems. They are changing industries like healthcare, finance, and transportation. Let’s go through the types of agents in AI and how useful they are.
Quick Summary
In this blog, we will read about the types of AI agents you interact with in your daily life. You will also read how they work, their key components and why they matter in everything from cybersecurity to gaming.
What are AI Agents?
An AI is a smart assistant who observes the environment, analyzes it and performs the tasks. These agents follow a sequence that includes sensing the environment, processing data , and acting based on defined goals. AI agents are key to smart systems, automating processes and solving problems. The types of agents vary. And that depends on their complexity and functions. But all share one goal which is making intelligent decisions.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be categorized into several types based on their functionality. Simple Reflex Agents operate by reacting to current conditions using predefined rules, making them suitable for straightforward tasks. Model-Based Agents utilize internal models of the environment to plan actions and handle more complex scenarios. Goal-Based Agents focus on achieving specific objectives, enabling them to make decisions aligned with long-term goals. Finally, Learning Agents improve their performance over time by learning from experience and adapting to new situations, making them highly versatile in dynamic environments.
1. Simple Reflex Agents
Simple reflex agents respond directly to environmental conditions. They follow “if-then" rules and act based on immediate input without considering past or future states. These agents make decisions quickly.
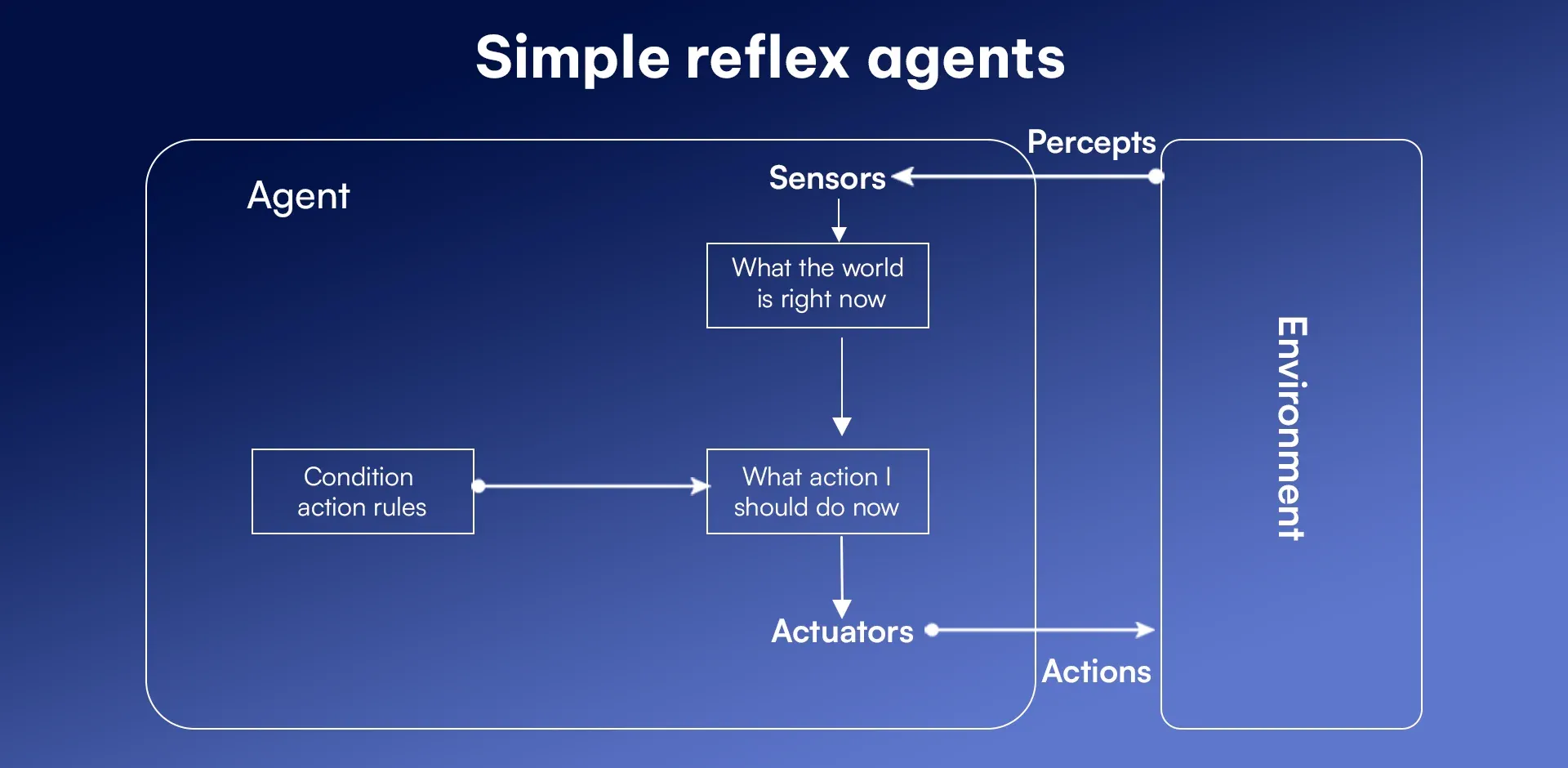
Key components:
- Sensors: It gathers data from the environment.
- Condition-action rules: It decides what action to take based on input.
- Actuators: It carries out the action.
Example: Thermostats adjust the temperature based on the current room condition.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
Model-based reflex agents are smarter as they consider the environment’s state. It also considers how it changes over time. These agents maintain an internal model that makes those models more sophisticated than simple reflex agents.
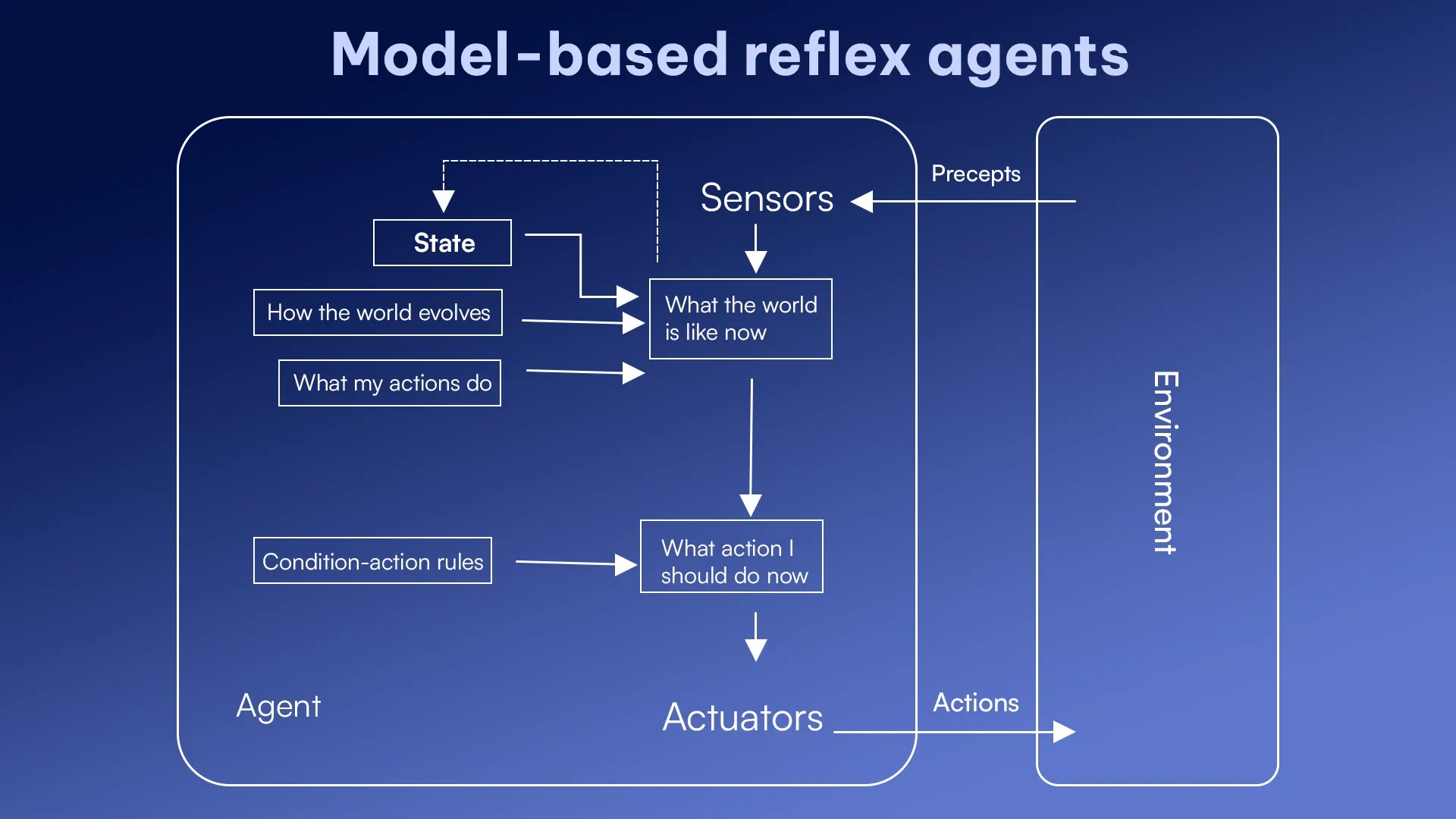
Key components:
- State tracker: It tracks current conditions.
- World Model: It represents how the environment behaves.
- Reasoning component: It decides the best action based on current and predicted states.
Example: Self-driving cars use model-based reflex systems to navigate roads safely.
3. Goal-Based Agents
Goal-based agents aim for specific objectives and can even make decisions to achieve them. These agents work towards precise goals which makes them more flexible and purposeful.
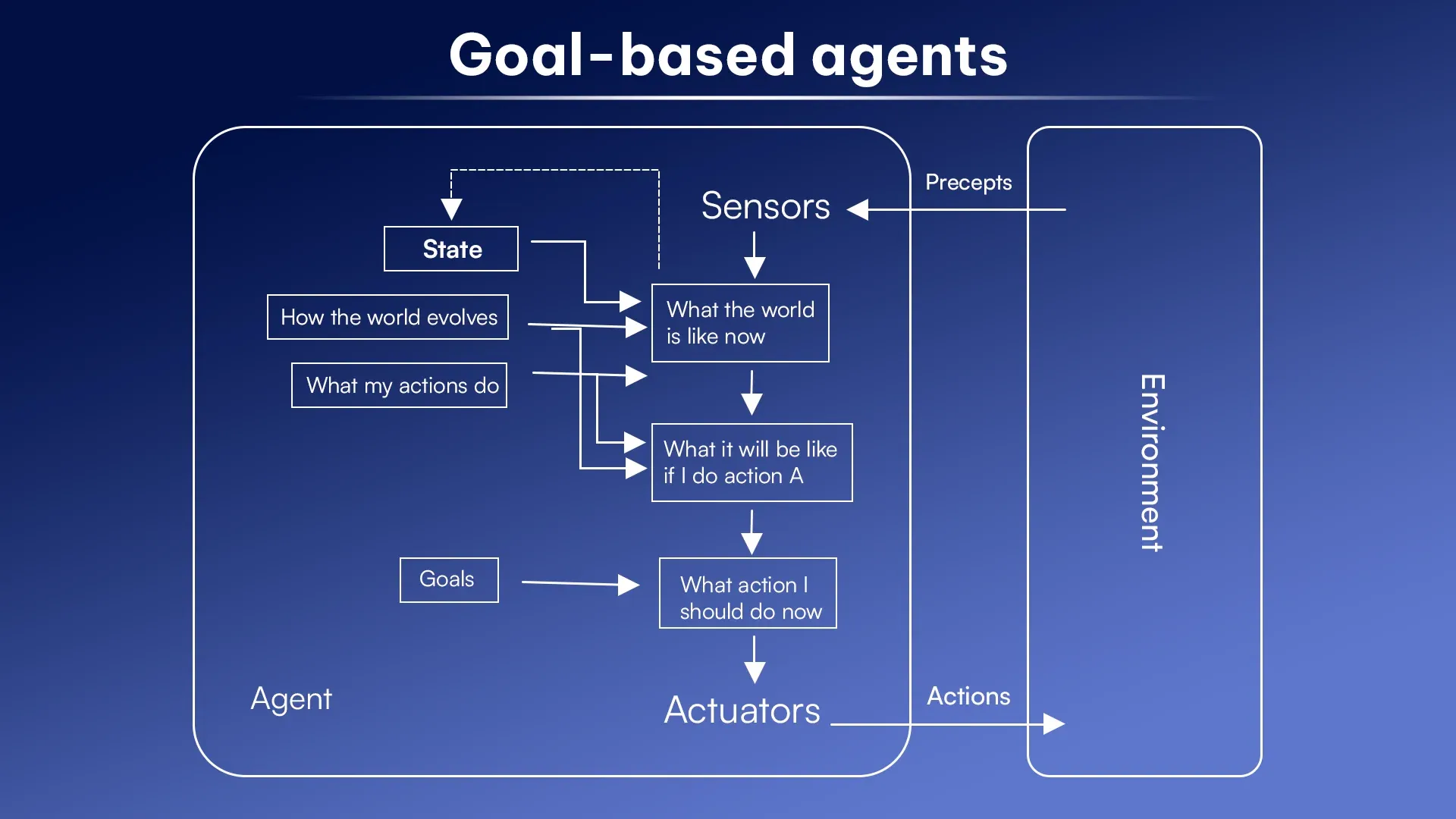
Key components:
- Goal state: It is the desired outcome where agents work toward.
- Planning mechanism: It plans actions to reach the goal.
- State evaluation: It measures progress toward the goal.
- Action selection: It chooses the next best step.
- World Model: It keeps track of environmental changes.
Example: A delivery drone plans and adjusts its route to deliver packages efficiently.
Also read: AI Agent vs AI Chatbot - What is the Main Difference?
4. Learning Agents
Learning agents grow their performance over time by learning from experiences. They adapt to new situations, adjust their objectives and improve their decision-making capabilities.
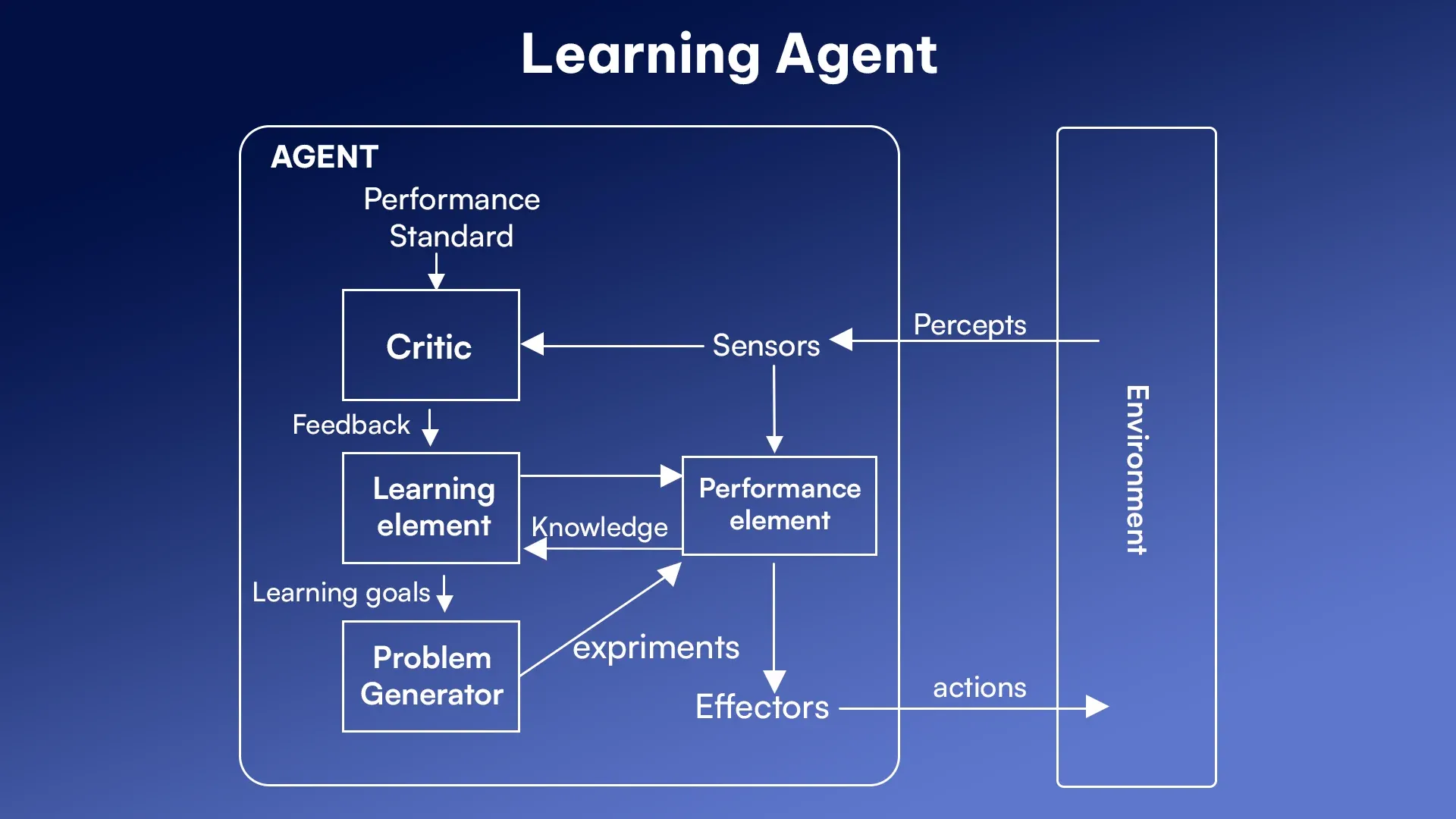
Key components:
- Performance elements: It executes tasks.
- Critic: Evaluates outcomes.
- Learning element: Identifies areas for improvement.
- Problem Generator: Suggests new challenges for better learning.
Example: Chatbots become more accurate as they interact with users.
5. Utility-Based Agents
Utility-based agents go beyond achieving goals. They aim to maximize happiness or satisfaction or utility. These agents make decisions based on what gives the most value in each situation. It ensures the best outcomes.
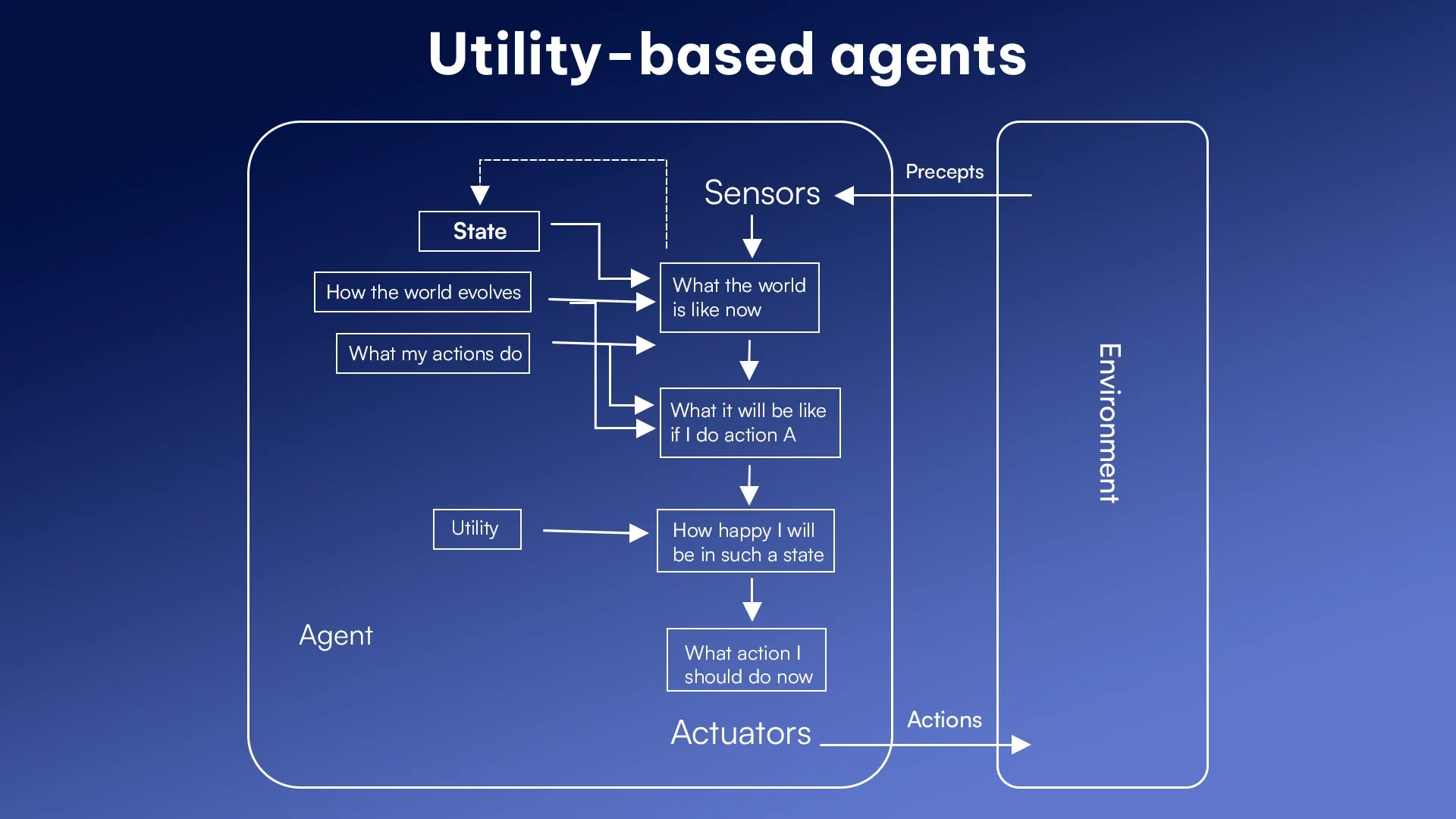
Key components:
- Utility function: It measures success based on user satisfaction.
- State evaluation: It rates the desirability of outcomes.
- Decision mechanism: It selects actions that optimize utility.
- Environment model: It tracks possible outcomes.
Example: Recommendation systems like Spotify suggest songs that match your music taste perfectly.
Structure of AI Agent
Explore the structure of AI agents, including components like perception, decision-making, and learning systems. Discover how AI agents operate and solve real-world problems effectively. AI agents are involved and applied in many fields. Those include:
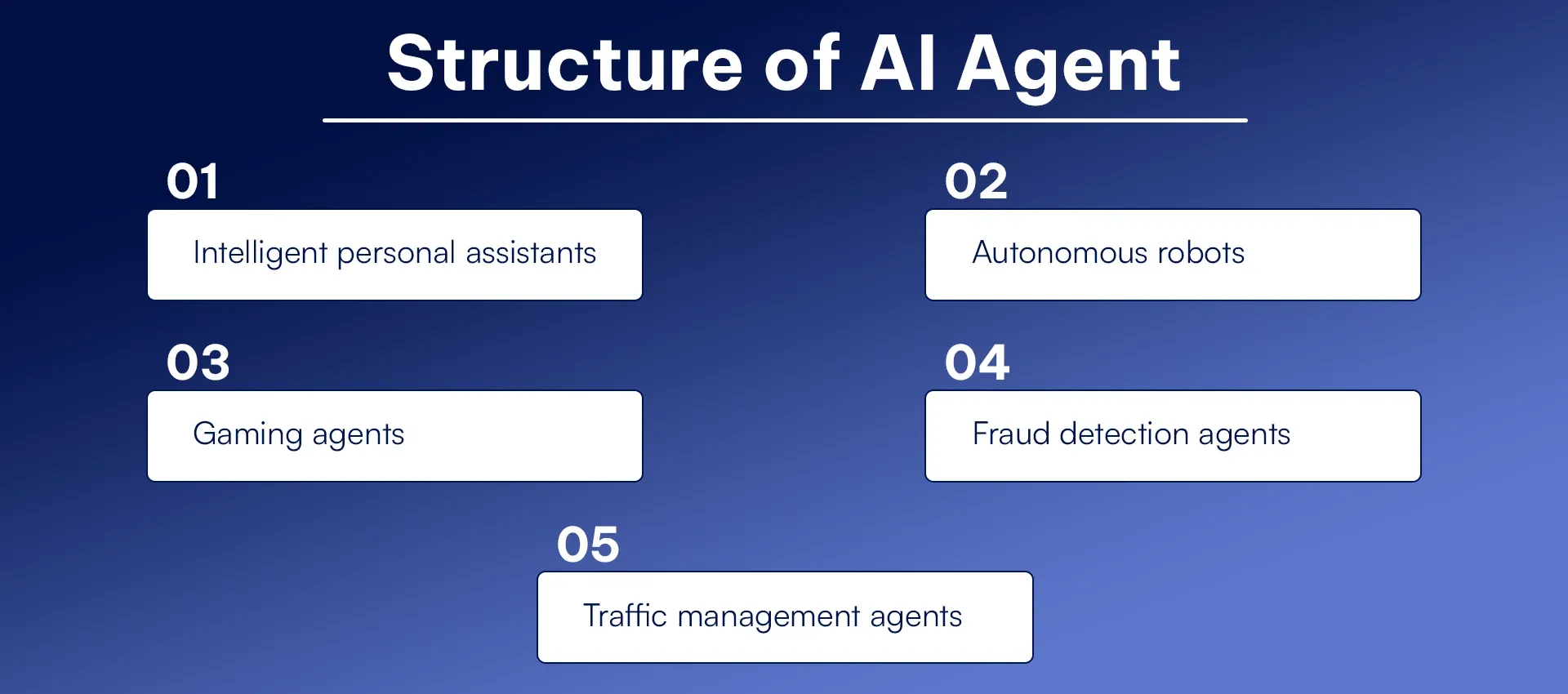
- Intelligent personal assistants: Alexa and Siri.
- Autonomous robots: Warehouse robots like Amazon’s Kiva.
- Gaming agents: AI opponents in video games.
- Fraud detection agents: Analyzing transactions for anomalies.
- Traffic management agents: Controlling traffic flow.
Other forms include a software agent, a human agent, and a robotic agent.
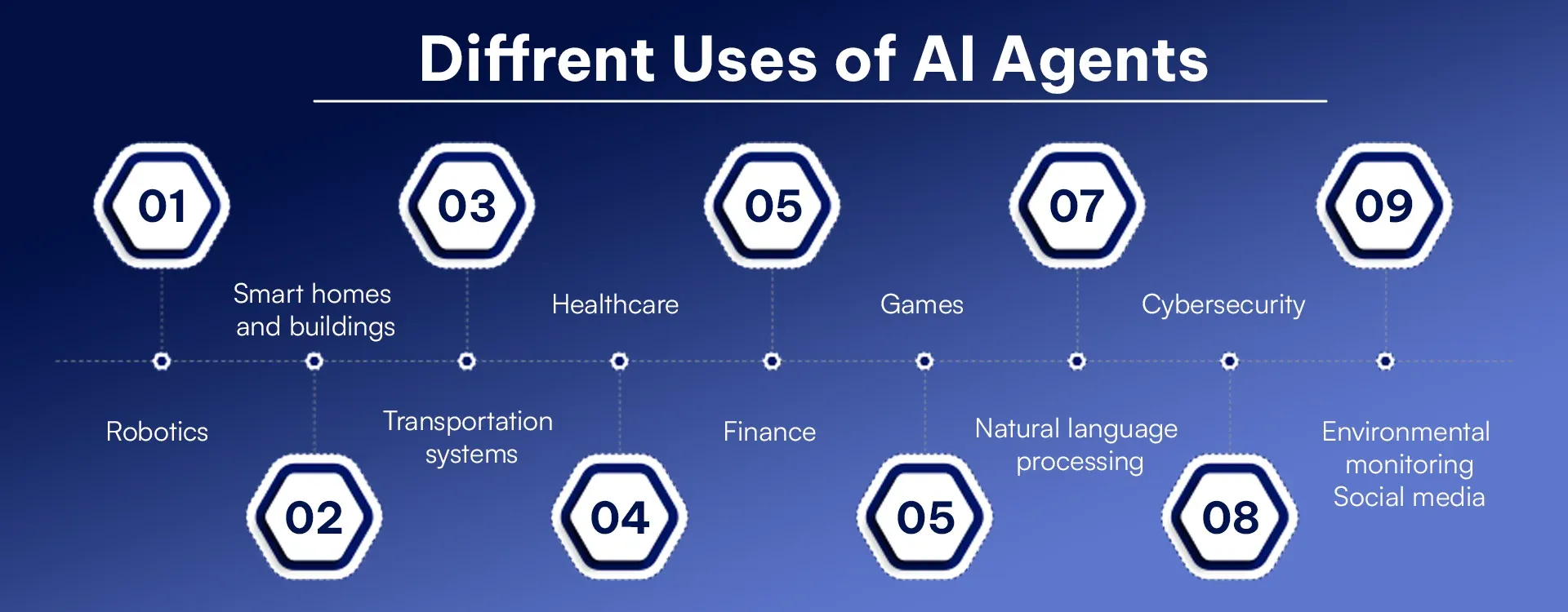
Different Uses of AI Agents
AI agents are versatile tools capable of performing tasks across industries. They automate customer support with chatbots, optimize workflows in business operations, enable personalized recommendations in e-commerce, assist in medical diagnostics, enhance financial analytics, and power virtual assistants for daily tasks. Their adaptability makes them invaluable in solving complex problems efficiently. AI agents are transforming various industries, such as:
-
Robotics: Automating manufacturing. Agents can be used in engaging a robot by controlling it and automating tasks in manufacturing and other sectors of industries.
-
Smart homes and buildings: Managing security, heating and lighting. Agents can be used to control security, lighting, heating, and other systems in smart homes and buildings which improve the use of energy.
-
Transportation systems: Powering autonomous vehicles. Agents can be used to manage the flow of traffic, optimize routes for autonomous vehicles and self-driving cars, and assist in logistics.
-
Healthcare: Diagnosing diseases and personalizing treatment. Agents can be used to monitor patients, give personalized treatments and improve healthcare resource allotment.
-
Finance: Detecting fraud and automating trading. Agents can be used for automating systems used for trading, fraud detection, and prevention of risk in the financial industry.
-
Games: Creating challenging AI opponents. Agents can be used to create intelligent players in games and to get better and more realistic experiences for players.
-
Natural language processing: Powering chatbots and translators. Agents can be applicable in language translation, knowledge-based systems and chatbots that interact with people using NLP.
-
Cybersecurity: Monitoring threats in real-time. Agents can be used to detect intrusions and analyze malware and network security threats. It ensures protection.
-
Environmental monitoring: Analyzing climate data. Agents can be used to monitor and safeguard natural resources, develop models to predict and analyze disaster risk management.
Conclusion
The agents of AI are transforming every industry today. They change the way we work, live, and interact with technology. Agents vary from simple reflex systems reacting to basic inputs to more complex multi-agent systems collaborating in real time. Such is what drives a lot of innovation.
Familiarization with the different types of AI agents unlocks their further applications within personal and professional life. From home management to better optimization of business operation or user experience, there exists an AI agent to ease things.
At Rejoice Hub, we specialize in creating custom AI agents tailored to your unique needs. Our solutions help businesses streamline operations, improve decision-making, and boost productivity. With our expertise, you can seamlessly integrate AI into your processes and take your business to the next level. Let us help you build the perfect AI agent to achieve your goals!
Rejoicehubllp will be able to assist you if you are interested in introducing AI agents into your business. We are a one-stop solution for bespoke AI tool development and the scaling of your current operations using advanced machine learning. Our cutting-edge AI/ML development services will empower your business with intelligent solutions to improve efficiency, drive growth, and elevate customer experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the most common AI agents?
Common types include simple reflex agents, learning agents, and utility-based agents.
2. What industries benefit most from AI agents?
Healthcare, finance, transportation, and gaming are the industries most benefited from AI agents.
3. How do multi-agent systems work?
They involve agents collaborating or competing based on predefined protocols and goals.
4. Why are hierarchical agents important?
They manage complex tasks efficiently by breaking them into smaller and coordinated subtasks.
