Have you ever thought about how AI produces those amazing, realistic pictures that are all over the internet? Or how certain apps can change your basic drawings into professional-looking art? The key to all this is generative adversarial networks, or simply GANs.
Honestly, when I first encountered GANs, I could not get over it. The whole thing looked as if it were a magic trick. But then I realized that the technology is really just an application of smart thinking to AI when I got to know the process a little better.
Let us consider some non-technical and common instances from our everyday lives as examples that are probably well recognized by you. Have you come across those apps that can add a few years to your face or make you look younger? That is GAN tech.
Or is it AI-generated portraits that are indistinguishable from real people but do not exist? Right, GANs again. Even some of the beautiful AI art shared on social media has been created by deploying these networks.
How Generative Adversarial Networks Work
So, what precisely is a generative adversarial network? I will simply put it up for you to understand.
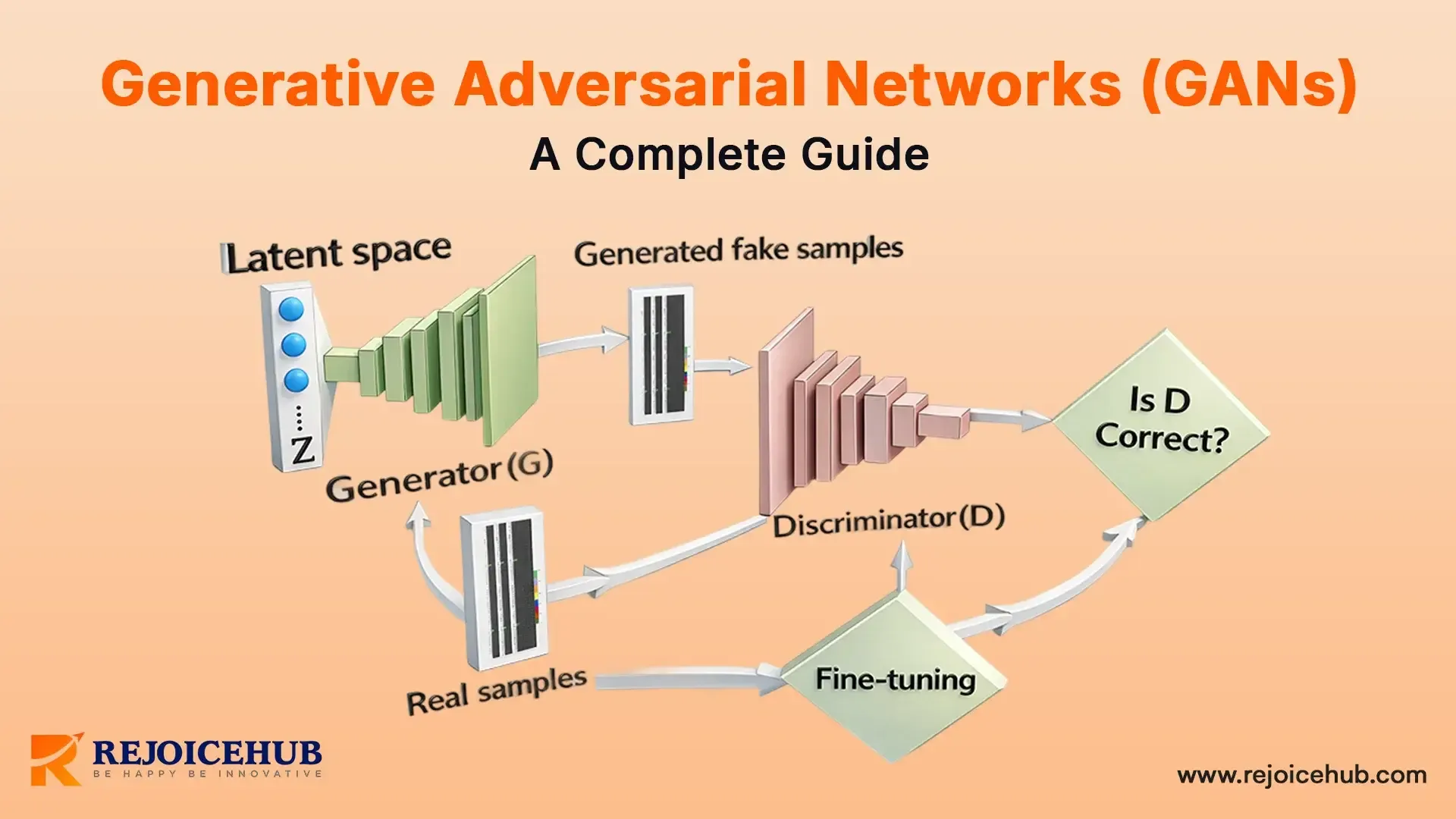
A GANs comprises two principal components that collaborate: the generator and the discriminator. I prefer to visualize them as an art forger and an art detective, respectively.
The discriminator: the role of the detective, in essence. Its duty is to scrutinize the data and then make a call whether it is real or fake. It takes a look at the real images and also the ones produced by the generator, doing its job and coming up with a verdict.
Step by step, let me take you through the training process. First off, the discriminator is fed real data and is allowed to learn the features that identify the "real". Next, the generator produces a batch of fake data and puts it through the discriminator.
That cycle goes on thousands of times. Each time, the generator is more realistic in data creation, and the discriminator is more expert in fake spotting. Ultimately, the generator reaches the point where even the discriminator does not have a high degree of confidence in drawing the line between real and fake data. That's when we considerthat the GAN technology has successfully learned to produce realistic outputs.
What is a generative adversarial network?
Confession, when I first saw the diagram of a GANs, it seemed very complicated to me. Rather, if the fundamental process is comprehended, it all turns out to be logical.
The structure's inception is at a point referred to as random noise. Picture this as complete disorder,
TV static, for instance. The noise is then introduced to the generator, which is actually a neural network that takes this chaos and outputs something reasonable, such as an image.
The fact that generative adversarial networks are AI is what sets them apart from traditional neural networks through this competitive dynamic. In the case of a common neural network, the model minimizes its error; thus, there is a single model. With the GAN, the two models are havingosing goals, and this leads to a much more refined learning process.
Types of Generative Adversarial Networks
To summarize, Ian Goodfellow introduced the first generative adversarial network (GAN), and since then, researchers have come up with many different types of GANs.

1. Vanilla GAN
Is the original version the one Goodfellow created? It's simple, making it great for understanding the basic concepts. However, it's not as powerful as the newer versions. Use a Vanilla GAN for simple image generation tasks or learning purposes.
2. DCGAN (Deep Convolutional GAN)
Introduced the use of convolutional layers. Convolutional networks are the best at image processing if you have good knowledge of computer vision. Therefore, they are widely accepted in the generation of faces, bedroom interiors, and other detailed images.
3. Conditional GAN (cGAN)
is a very handy type of GAN due to its flexibility, which is why I like it the most. In contrast to basic GANs that randomly produce outputs, conditional GANs allow you to decide what will be generated. For example, do you want a cat image instead of a dog?
4. CycleGAN
Performs a magical operation of transforming images from one domain to another without the use of paired samples. The pictures can be transformed from photographs to paintings, from summer landscapes to winter ones, or from horses to zebras. The use of this technique by photographers to render their images in different artistic styles has resulted in some mind-blowing works.
5. StyleGAN
The most renowned GAN from NVIDIA is undoubtedly the one for generating realistic-looking human faces. You might have encountered the images of "This Person Does Not Exist"? They are the result of StyleGAN. StyleGAN allows the user to have an amazing manipulation of the style and characteristics of the produced images. Fashion designers and game developers appreciate StyleGAN for making character designs.
6. BigGAN
The utilization of large models trained on colossal datasets brings about a revolution in AI technologies. The output of such models is exceptionally detailed and varied. Along with high-end computing, it is still being used in research and by companies that have a great demand for high-quality image generation.
Applications of GANs in Real Life
When individuals inquire of me about where they can find GAN technology in their everyday lives, I respond to them- it is likely not as far away as you would have imagined!
It is most likely that image production and improvement is the most apparent usage. Whenever you decide to use an app to sharpen your image or remove blur or add resolution, chances are high that GANs are doing their work in the background. Your phone's portrait mode? That usually utilizes AI generative adversarial network methods to generate that desirable blurred background effect.
GANs are also changing the gaming and virtual world, in case you are a gamer. They are utilized by game developers to create the authentic look of the textures, to make various characters, and even to create the whole virtual world. The following time you feel amazed at the degree of realism displayed by a game, it is likely that some GAN magic is at work.
Also Read: What Is Generative Design? Process, Benefits, and Use Cases
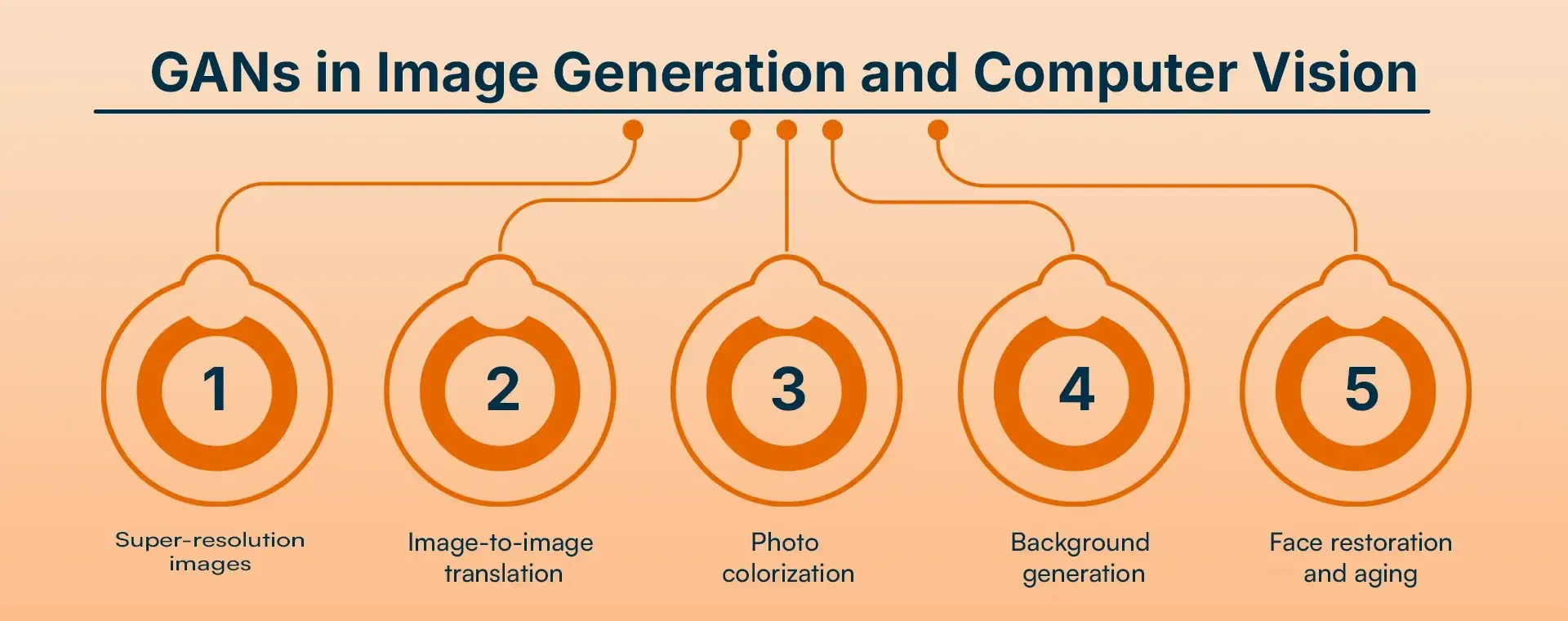
GANs in Image Generation and Computer Vision
Now I will provide you with some of the computer vision applications where a generative adversarial network can be used.
-
Super-resolution images
It is most likely my favorite GAN application. You know, in movies, they zoom in on the security camera shots and just turn them into crystal clear? That is a fiction, but GANs are drawing it nearer to reality. They can use a low-resolution, blurry image and fill in the lost details intelligently to come up with a much sharper image.
-
Image-to-image translation
transforms pictures between styles. You can transform an unpolished sketch into a photo-realistic picture, or even satellite pictures into a map picture. This is used by architects to make simple floor plans appear like real rooms. It is similar to having a universal translator except that it does not deal with languages but rather images.
-
Photo colorization
is what it took hours of human labor to do. More importantly, GANs are now capable of adding natural colors to photographs that are in black and white. I have applied it to colorize old relatives' photos, and the outcomes were unbelievable. It is not a mere guess of the AI, but an educated guess based on millions of colored pictures to have a clue what things are supposed to be colored with.
-
Background generation
has become a necessity for content creators. Require a tropical beach background for your video call? It is possible to generate one that is real with the help of GANs. GANs have been applied in product photography, where photographers can position products in various settings without incurring the high costs of conducting photoshoots.
-
Face restoration and aging
Applications are useful and entertaining. In addition to those older applications that I described above, GANs are also employed to reconstruct old photographs when they are damaged, and faces become clear and detailed once more. Even the law enforcement agencies employ the same technology to age the photos of missing individuals.
Advantages of Generative Adversarial Networks
I have worked with various AI-generated adversarial networks, and now I can say that there are several key advantages that I appreciate.
High-quality synthetic data generation is probably the most significant benefit. Almost real data can be generated by GANs. The situation is very favorable for those areas where getting real data is either very costly or cannot be done at all. Would you like to have a million training images for your AI mode, but can only get a thousand? GANs come in to help.
GANs outperform traditional generative models such as basic neural networks or simple statistical approaches. The adversarial training process pushes the generator to constantly improve, leading to outputs that are more diverse, more realistic, and more suitable for real-world applications.
Limitations and Challenges of GANs
I really adore GAN technology, but at the same time, I have to admit its limitations. Knowing these difficulties helps one to realize when to apply GANs and when to seek other options.
The issue with mode collapse is very annoying. Most of the time, the generator gets to an output type that keeps on deceiving the discriminator, and from there, it continues to produce the same thing indefinitely. Just think of a scenario where you train a GAN to produce faces, but in the end, you only get faces of the same person. That is what they call mode collapse,se and it is definitely a very big problem to resolve.
Another problem is that trainer instability is a real pain. Do you remember that competitive scenario I told you? Sometimes the equilibrium shifts too much in one way. If the discriminator becomes too powerful too fast, the generator won't develop its skill properly, and if the generator becomes too skillful, the discriminator stops getting better. Therefore, attaining the right balance requires accurate tuning and, frequently, a lot of trial and error.
GANs vs Other Generative Models
Generative models often let you choose between various options, one of them being generative adversarial networks. I will compare them to other popular methods.
The first comparison is GANs vs Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). VAEs reduce data to a small representation first, then expand it back and use it for the generation of new samples. They are considered to be more stable during training than GANs, i.e., they do not oscillate between modes and produce even more varied outputs, but the pictures are still lower in quality than those coming from GANs.
The present-day hot comparison point is GANs vs Diffusion Models. The new technology that has been the behind-the-scenes facilitator of DALL-E, and also Stable Diffusion, is the diffusion model.
In conclusion, what is the better generative model? With all honesty, it is up to the case at hand. GANs are perfect for applications that need instant resolutions and longest latency times. Currently, diffusion models are the ones that offer the most stable training and ease of use. For certain tasks like anomaly detection and data compression, autoencoders might just be the right choice. No single winner exists; various tools for different jobs are available.
Future of GANs in Artificial Intelligence
In the future, I am looking forward to the direction of the generative adversarial networks AI technology.
The GANs in combination with diffusion models represent one promising direction. Scientists are researching hybrid solutions that can combine diffusion models with the speed of GANs. Consider having the best of both worlds- fast generation where training is stable, and the products are varied.
Ethical AI and regulations will gain more and more importance. Already, we are witnessing companies come up with watermarking techniques to detect GAN-generated content.
It is believed that the future of AI-generated creativity will be where GANs will collaborate with human beings and not substitute them. Artists will be able to use AI tools of generative adversarial networks to test ideas much faster, musicians will compose new sounds, and writers may rely on text-based GANs and overcome creative blocks. The technology will not suppress human creativity, but rather increase it.
Conclusion
After thoroughly examining generative adversarial networks, I hope you can grasp their significance in contemporary artificial intelligence.
We went through a lot of details crosswise. Initially, we dealt with the ground information of what a GANs is two neural networks engaging in a rivalry to elevate each other to higher standards. Following that, we proceeded to the various types of GANs, starting with the initial Vanilla GAN, leading up to sophisticated models like StyleGAN and BigGAN. We also examined the various fields all over the world where these networks were applied, from the medical sector to gaming.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How are GANs used in image generation?
GANs generate images by learning patterns from real photos, then creating new, realistic images. They're used for face creation, art generation, photo restoration, and super-resolution enhancement.
2. Can GANs create realistic human faces?
Yes, GANs like StyleGAN create photorealistic human faces that don't exist. The "This Person Does Not Exist" website showcases AI-generated faces that look completely real and natural.
3. How is AI generative adversarial network used in medicine?
Medical GANs generate synthetic patient data, enhance medical imaging quality, detect diseases from scans, create training datasets, and help develop new diagnostic tools while protecting patient privacy.
4. What are the types of generative adversarial networks?
Common types include Vanilla GAN, DCGAN, Conditional GAN, CycleGAN, StyleGAN, and BigGAN. Each type serves different purposes, like image translation, style transfer, or high-resolution face generation.
5. Who invented generative adversarial networks AI?
Ian Goodfellow invented generative adversarial networks in 2014. His breakthrough concept introduced the competitive training approach that revolutionized AI image generation and creative applications.
6. What is a Conditional GAN (cGAN)?
A Conditional GAN lets you control what the network generates by providing specific inputs. You can choose to create particular objects, styles, or features instead of random outputs.
7. What are the challenges of training generative adversarial networks?
Training challenges include mode collapse, unstable learning, balancing generator and discriminator power, requiring significant computing resources, and achieving consistent, high-quality results across different data types.
8. What is StyleGAN used for?
StyleGAN is used for generating ultra-realistic human faces, character design in games, fashion visualization, portrait creation, and controlling specific features like age, expression, or hairstyle.
9. What is the future of generative adversarial networks AI?
The future includes faster training methods, hybrid models combining GANs with diffusion technology, better ethical safeguards, creative collaboration tools, and more accessible applications for everyday users.
10. What is the difference between GANs and other AI models?
Unlike traditional neural networks, GANs use two competing models instead of one. This adversarial process creates more realistic outputs compared to autoencoders or basic generative models.
